
Apparent Resolution Enhancement for Animations, SCCG 2011
Apparent Resolution Enhancement for Animations
Krzysztof Templin1,2
Piotr Didyk2
Tobias Ritschel3
Elmar Eisemann3
Karol Myszkowski2
Hans-Peter Seidel2
1 University of Wroclaw, Poland
2 MPI Informatik, Germany
3 Telecom ParisTech, France
Apparent Resolution Enhancement for Animations
Krzysztof Templin1,2 Piotr Didyk2 Tobias Ritschel3 Elmar Eisemann3 Karol Myszkowski2 Hans-Peter Seidel2
1 University of Wroclaw, Poland 2 MPI Informatik, Germany 3 Telecom ParisTech, France

Abstract
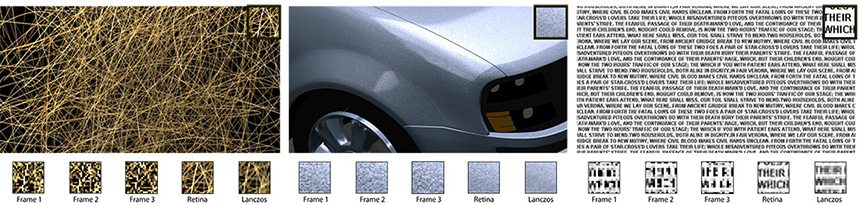
Presenting the variety of high resolution images captured by high-quality devices, or generated on the computer, is challenging due to the limited resolution of current display devices. Our recent work addressed this problem by taking into account human perception. By applying a specific motion to a high-resolution image shown on a low-resolution display device, human eye tracking and integration could be exploited to achieve apparent resolution enhancement. To this end, the high-resolution image is decomposed into a sequence of temporally varying low-resolution images that are displayed at high refresh rates. However, this approach is limited to a specific class of simple or constant movements, i.e. ''panning''. In this work, we generalize this idea to arbitrary motions, as well as to videos with arbitrary motion flow. The resulting image sequences are compared to a range of other down-sampling methods.
Materials for Download
|
Related Publications
 |
Apparent Display Resolution Enhancement for Moving Images
Piotr Didyk, Elmar Eisemann, Tobias Ritschel, Karol Myszkowski, Hans-Peter Seidel ACM Transactions on Graphics 29(4) (Proceedings SIGGRAPH 2010, Los Angeles).
|
Citation
Krzysztof Templin, Piotr Didyk, Tobias Ritschel, Elmar Eisemann, Karol Myszkowski, Hans-Peter Seidel
Apparent Resolution Enhancement for Animations
Proceedings of the 27th Spring Conference on Computer Graphics, 28-30 April 2011, Vinicne, Slovakia
@inproceedings{TemplinDREMS2011,
author = { Krzysztof Templin and
Piotr Didyk and
Tobias Ritschel and
Elmar Eisemann and
Karol Myszkowski and
Hans-Peter Seidel
},
title = {Apparent Resolution Enhancement for Animations},
booktitle = {Proc. of the 27th Spring Conference on Computer Graphics},
pages = {85--92},
address = {Vinicne, Slovakia},
year = {2011}
}
© ACM, (2011). This is the author's version of the work. It is posted here by permission of ACM for your personal use. Not for redistribution.
The definitive version was published in Proc. of the 27th Spring Conference on Computer Graphics, (April 28--30, 2011).