
3. Global Illumination Methods
3.1 Radiosity Methods
3.1.1-3 Radiosity for Lambertian Environments

Four stages of progressive image quality refinement using the hierarchical
radiosity algorithm with clustering described in Sections 3.1.1-3.
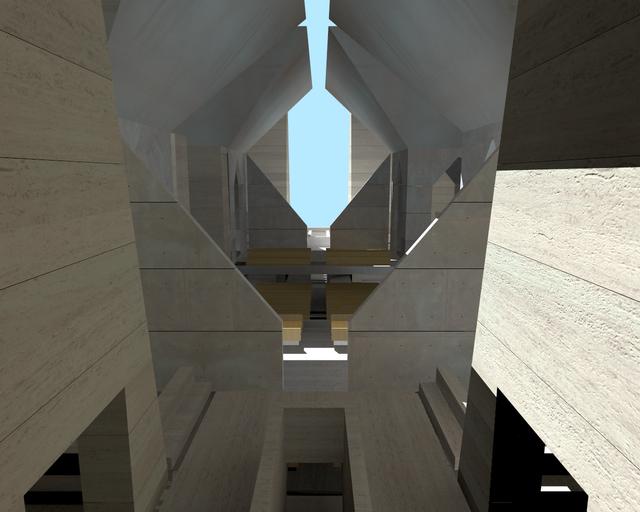

Radiosity solution for complex architectural environment
using the techniques proposed in Sections 3.1.1-3.
3.1.4 Radiosity for Non-Lambertian Environments
The "image method" used for primary lights. The bottom-left
image was obtained using the traditional hierarchical radiosity algorithm
described in Sections 3.1.1-3. The bottom-right image was obtained using
the radiosity algorithm extended with the "image method" described in Section
3.1.4. The corresponding mesh used for the radiosity solution is shown
in the top-left image. The top-right image was obtained using a hybrid
of radiosity and ray tracing solutions discussed in Section 3.4.
Clustering of secondary "virtual lights" for the image
method. In the left image the mirror was ignored during the shooting radiosity
iteration, while it was considered in the right image. Note the complex
light path that was simulated in the latter case: the face is mostly illuminated
by light emitted by the red lamp, which is reflected by the table and then
by the mirror.
3.2 Stochastic Methods
3.2.4 Enhanced Density Estimation Methods
 |
 |
|
|
|
 |
1
10
100
1000 |
|
error |
method |
for ENN |
method |
for NN |
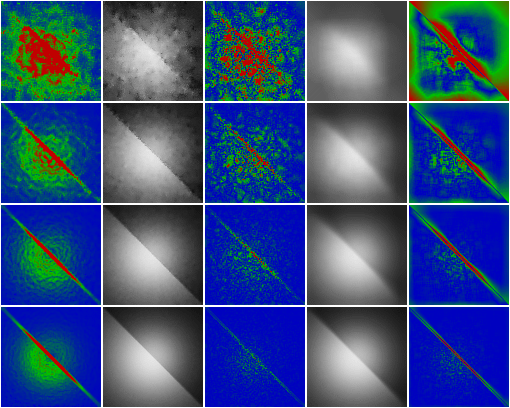
Comparison of illumination textures (IT) computed using the ENN
and NN methods for the lighting pattern shown in Figure 3b. Also, the distribution
of the estimated local error using equation (3.9), and the actual local
error computed for every texel independently are shown (the average actual
error values are depicted in Figure 3a as the RMSerror
plots). The meaning of the images is as follows: distribution of
the estimated error (the first column), illumination textures and the corresponding
distribution of the actual error for the ENN and NN methods (the
second and third columns, and the last two columns, respectively). The
rows of images correspond to an average number of 1, 10, 100, and
1000 photons per texel. Color scale for the locally measured relative reconstruction
error is as follows: blue up to 10%, green up to 20%, red 20% and more.
As can be seen the ENN method leads to smaller local error values and a
better reconstruction of discontinuities in the lighting function than
the NN method.
3.2.5 Density Estimation at Interactive Speeds
 |
 |
|
|
|
3.4 Hybrid Methods
An example of animation computed using a hybrid
of the radiosity and ray tracing methods. Note that this animation is presented
in the QuickTime format, which requires a specialized animation viewer
supporting this format, e.g., QuickTime plug-in for web browsers available
under the URL: http://www.apple.com/quicktime/.