Release 9.2 for Windows
Part Number A95496-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle Services for Microsoft Transaction Server Developer's Guide Release 9.2 for Windows Part Number A95496-01 |
|
This chapter describes installation and migration requirements for the Microsoft Transaction Server and Oracle database server environment.
This chapter contains these topics:
Figure 2-1 shows a typical Microsoft Transaction Server and multiple database server installation layout.
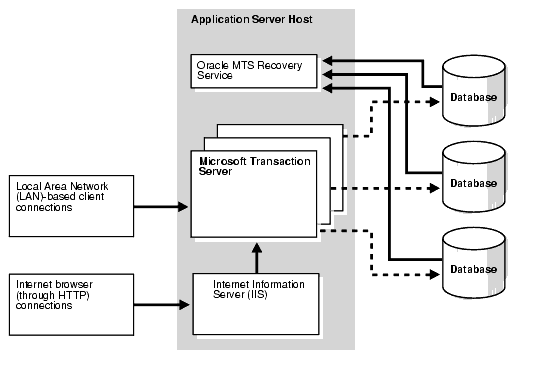
Table 2-1 lists the Oracle and non-Oracle products you must install. After reviewing the installation requirements, see the Oracle9i Database Installation Guide for Windows for instructions on installing the required Oracle products. Key guidelines to understand are:
|
Note: Microsoft Transaction Server integration with a database server is not currently supported on Windows 95 or Windows 98. |
| On This Computer... | Oracle Products | Non-Oracle Products |
|---|---|---|
|
Client computer |
||
|
Windows NT computer where Microsoft Transaction Server is installed |
|
|
|
Computer where the database server is installed |
|
| 1 See the Oracle9i Database Installation Guide for Windows for installation instructions. During installation, you are prompted to enter the port number on which the Oracle MTS Recovery Service will listen for requests to resolve in-doubt transactions. 2 Oracle Net Services is automatically installed with Oracle Services for Microsoft Transaction Server. 3 Release 8.1.3 of OO4O, Oracle ODBC Driver, Oracle Provider for OLE DB, and OCI are only required if you are building or using components with which they are required. 4 An applications server like IIS is not required, but is beneficial if using Microsoft Transaction Server. Install the applications server on the same computer as Microsoft Transaction Server. The applications server you choose must support extensions. 5 Microsoft Transaction Server is currently available as part of the Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Option Pack. Microsoft Management Console is automatically installed with Microsoft Transaction Server. 6 After installing Microsoft Transaction Server 2.0, Oracle Corporation recommends that you install Windows NT 4.0 Service Pack 5 or higher. You must re-install any service packs installed prior to Microsoft Transaction Server 2.0 installation. 7 If the database server is a release prior to 8.0.6, you cannot use the integration described in this guide. See "Using Microsoft's Oracle ODBC Driver" for a description of what functionality is available for pre-8.0.6 database servers. |
Starting with Oracle release 1 (9.0.1), you were no longer required to create the Oracle Service for MTS. However, before proceeding to uninstall Oracle Services for Microsoft Transaction Server, you must use the Oracle Manager for MTS Services snap-in in the Microsoft Management Console Explorer to delete the existing Oracle Service. Table 2-2 shows the procedures to follow.
| If You... | Then... | See... |
|---|---|---|
|
Migrate the release 8.1.x database server to the current release and create a new installation of release 9.2 |
|
"Deleting an Oracle Service with the Oracle Manager for MTS Services Snap-In" "Using the Registry to Manually Delete the Oracle Service" if you have already deleted the database server |
|
- |
"Deleting Roles and Privileges of an Inactive Oracle Service User" |
|
|
- |
|
The Oracle9i Database Installation Guide for Windows |
|
- |
Chapter 3, "Managing Recovery Scenarios" |
You must use the Oracle Manager for MTS Services snap-in in the Microsoft Management Console Explorer to delete the Oracle Service. Deleting the Oracle Service in any other way (such as with the keyboard's Delete button) causes data inconsistencies in the database server. These inconsistencies require the database administrator to manually commit or terminate transactions that did not successfully complete or recover. Before deleting the Oracle Service, ensure that all transactions are resolved by performing the following tasks.
To stop the Oracle Service:
The Microsoft Management Console appears.
MTSDEMO in this example):
A menu appears with several options.
To stop and restart the database server:
C:\> sqlplus /NOLOG
SYSDBA:SQL> CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
SQL> SHUTDOWN
SQL> STARTUP
SQL> EXIT
To restart the Oracle Service:
The Microsoft Management Console appears.
A menu appears with several options.
A message indicates that the Oracle Service started.
To monitor the Oracle Service trace files:
2515156: [2096] OracleMTSService - Accepting new enlistment requests.
This file is located in ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\oramts\trace.
A message indicates that the Oracle Service stopped.
To delete Oracle Service table information:
C:\> sqlplus /NOLOG
SYSDBA:SQL> CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
SQL> DROP TABLE mtsadmin_username.mts_proxy_info;
where mtsadmin_username is the Oracle Service user (for example, mtssys).
SQL> COMMIT;
To delete the Oracle Service:
The Microsoft Management Console appears.
A menu appears with several options.
| If a Message Indicates That... | Go To... |
|---|---|
|
The Oracle Service was successfully deleted. |
"Deleting Roles and Privileges of an Inactive Oracle Service User" |
|
The Oracle Service was not deleted. |
Ensure that you delete the roles and privileges assigned to an Oracle Service user that you no longer use or whose service you have deleted.
To delete roles and privileges of an inactive Oracle Service user:
ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\oramts\admin.revokeuser.sql with a text editor.mts_user with the username from which to revoke roles and privileges.
revokeuser.sql.C:\> sqlplus /NOLOG
SYSDBA:SQL> CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
SQL> @ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\oramts\admin\revokeuser.sql;
The roles and privileges for the user are deleted.
SQL> EXIT
Before deleting the Oracle Service, it must be cleanly disassociated from the database server to which it connects. Sometimes this disassociation fails. Follow the instructions in this section only if:
Table 2-3 describes the scenarios in which the Oracle Manager for MTS Services snap-in of the Microsoft Management Console Explorer can fail to delete or modify the Oracle Service.
To manually delete Oracle Service with the registry:
C:\> regedt32
The Registry Editor window appears.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE window.
Go to System\CurrentControlSet\Services\OracleMTSServicen.
where n is the number of the Oracle Service.
The right-hand side of the window shows various parameters and values associated with OracleMTSServicen, including those listed in the following table:
| Parameter | This Parameter Contains... |
|---|---|
|
|
The Oracle Service username |
|
|
The password for the Oracle Service username (encrypted in the registry) |
|
|
The net service name for the Oracle Service to use in connecting to the database server |
C:\> sqlplus /NOLOG
CONNECT as username/password@net_service_name
where net_service_name is the net service name for connecting to the database. The password is stored in the registry in encrypted form. Use plain text passwords when connecting with SQL*Plus.
SQL> SELECT NAME, DBID FROM V$DATABASE;
which displays information similar to the following:
NAME DBID --------------------- ORCL 12345678
ORAMTS_DBNAME (ORCL in this example) and ORAMTS_DBID (12345678 in this example).SQL> SELECT rmguid FROM mts_proxy_info;
which displays information similar to the following:
RMGUID ------------------------- 2320b23e93e09fff02a231974
ORAMTS_RMGUID.If not all values match, the database server is not the same one to which the Oracle Service connects. If you continue, Oracle Service installation on the database server fails. This can leave the database server in an inconsistent state that requires database administrator intervention to correct. The reason SQL*Plus connected to a different database server than the Oracle Service is mismatching tnsnames.ora files.
SQL> DELETE FROM mts_proxy_info; SQL> COMMIT;
SQL> EXIT
To delete the OracleMTSServicen service:
The Microsoft Management Console appears.
A menu appears with several options.
If successful, a message indicates that the Oracle Service was deleted.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE window, delete the following key:
\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\OracleMTSServicen.
where n is the number of the Oracle Service.
|
 Copyright © 1996, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|